This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricate tapestry of Rhode Island's crime rate, offering critical insights into current trends and future projections for 2025-2026. We explore the factors shaping public safety and provide data-driven perspectives for informed understanding.
Understanding Rhode Island Crime Trends
The landscape of crime in any region is a dynamic entity, constantly shaped by a confluence of socioeconomic, demographic, and policy-driven factors. For Rhode Island, the "Ocean State," understanding its crime rate trends requires a nuanced approach that looks beyond simple statistics to uncover the underlying narratives. Over the past decade, like many states, Rhode Island has experienced fluctuations in its crime indices. While overall crime rates have seen periods of decline, specific categories may exhibit different trajectories. Factors such as economic stability, unemployment rates, educational attainment, and the effectiveness of law enforcement strategies all play a significant role in influencing the safety and security of its communities. This analysis aims to provide a detailed examination of these trends, focusing on the most recent data available for the 2025-2026 period, offering a clear picture of the current state of public safety in Rhode Island. We will dissect various crime types, explore contributing elements, and compare the state's performance against national benchmarks to offer a holistic view.
Recent Crime Statistics: 2025-2026
The most critical aspect of understanding crime trends is to examine the latest available statistics. For the 2025-2026 period, preliminary data from the Rhode Island Department of Public Safety and other relevant agencies paint a complex picture. While a complete year-end report for 2026 will become available later, current indicators suggest a mixed performance across different crime categories.
Overall, the state has continued to see a general stabilization, with some indicators pointing towards modest decreases in certain types of offenses. However, this broad trend masks more specific shifts that warrant closer examination. For instance, while property crimes might show a downward trend, certain violent crime incidents could be experiencing an uptick, or vice versa. The reporting of crime is also a critical factor; increased reporting due to enhanced community trust or new data collection methods can sometimes influence statistics, making direct year-over-year comparisons require careful interpretation.
It is crucial to rely on official sources for the most accurate data. Agencies like the FBI's Uniform Crime Reporting (UCR) Program and state-level departments of justice are primary conduits for this information. For 2025-2026, we anticipate that the data will reflect ongoing efforts in community policing, targeted interventions for at-risk populations, and the continued impact of legislative changes related to public safety. The following sections will break down these statistics by crime category, providing a more granular understanding of the situation.
Key Crime Categories and Their Trajectory
To truly grasp the nuances of Rhode Island's crime rate, it's essential to dissect it into its constituent parts. Different types of crime have unique drivers and exhibit distinct trends. This section will explore the trajectory of major crime categories, providing insights into their prevalence and potential contributing factors.
Violent Crime Analysis
Violent crime, encompassing offenses such as murder, rape, robbery, and aggravated assault, is a primary concern for any community. For Rhode Island in the 2025-2026 period, the trends in violent crime are a mixed bag. Preliminary reports suggest a slight increase in aggravated assaults, potentially linked to interpersonal disputes and gang-related activities in specific urban pockets. Robbery rates, however, appear to be holding steady or showing a marginal decrease, possibly due to enhanced surveillance and proactive policing in commercial areas.
Homicide rates, while generally low in Rhode Island compared to national averages, have seen some localized spikes in recent years, which law enforcement agencies are actively working to address through targeted investigations and community engagement. Rape statistics are often subject to reporting fluctuations, but efforts to encourage reporting and improve victim support services are ongoing. The overall picture for violent crime indicates a need for continued vigilance and targeted interventions, particularly in areas identified as high-risk. The factors influencing these rates are complex, ranging from socioeconomic pressures to the availability of illicit substances.
Property Crime Trends
Property crimes, including burglary, larceny-theft, motor vehicle theft, and arson, constitute a significant portion of reported offenses. In Rhode Island for 2025-2026, property crime rates have generally shown a positive trend, with a noticeable decline in burglaries and larceny-thefts. This is often attributed to improved security measures in homes and businesses, increased public awareness campaigns about theft prevention, and more effective policing strategies that focus on deterring and apprehending property offenders.
Motor vehicle theft, a persistent issue in many urban areas, has seen some fluctuations. While overall rates might be down, specific models or areas may still be targeted. The rise of organized retail crime also presents a challenge, with coordinated shoplifting rings impacting businesses. Arson incidents, though relatively rare, are closely monitored due to their destructive potential. The general downward trend in property crime is a positive indicator for the state's overall safety and economic well-being, suggesting that preventative measures and law enforcement efforts are yielding results.
Drug-Related Offenses
The opioid crisis and the broader issue of substance abuse continue to cast a long shadow over public safety in Rhode Island, as they do across the nation. Drug-related offenses, encompassing possession, distribution, and manufacturing of illegal substances, remain a significant area of concern. For 2025-2026, data indicates a persistent challenge with drug-related arrests, particularly those involving synthetic opioids and stimulants.
While law enforcement continues to focus on interdiction and prosecution, there is also a growing emphasis on treatment and rehabilitation programs. The interplay between drug abuse and other criminal activities, such as property crime and violent offenses committed to fund addiction, is well-documented. Addressing drug-related offenses requires a multi-faceted approach that includes robust law enforcement, public health initiatives, and community support systems. The effectiveness of these combined strategies will be a key determinant in future trends.
Cybercrime and Emerging Threats
In the digital age, crime is increasingly moving online. Cybercrime, including identity theft, online fraud, phishing scams, and ransomware attacks, poses a growing threat to individuals and businesses in Rhode Island. While precise statistics for cybercrime are often harder to aggregate due to varying reporting mechanisms and the transnational nature of many offenses, law enforcement agencies are dedicating more resources to combating these digital threats.
For 2025-2026, reports indicate a steady increase in reported incidents of online fraud and identity theft, particularly targeting vulnerable populations like the elderly. Businesses are also facing sophisticated ransomware attacks that can cripple operations. The Rhode Island State Police and local police departments are enhancing their cybercrime units, collaborating with federal agencies, and conducting public awareness campaigns to educate residents on how to protect themselves from online scams. The evolving nature of technology means that cybercrime will continue to be a significant challenge, requiring continuous adaptation of prevention and enforcement strategies.
Factors Influencing Rhode Island Crime Rates
Crime rates are not arbitrary; they are the product of complex interactions between various societal factors. Understanding these influences is crucial for developing effective crime prevention and reduction strategies. This section explores the key elements that contribute to the crime landscape in Rhode Island.
Socioeconomic Indicators
Socioeconomic conditions are intrinsically linked to crime rates. Factors such as poverty, unemployment, income inequality, and lack of educational opportunities can create environments where crime is more likely to flourish. In Rhode Island, areas with higher poverty rates and lower median incomes often experience disproportionately higher rates of certain types of crime, particularly property and violent offenses.
The economic climate of 2025-2026, including inflation, job market stability, and access to affordable housing, plays a direct role. When individuals face significant economic hardship, they may be more susceptible to engaging in criminal activities out of desperation or lack of viable alternatives. Conversely, robust economic growth, job creation, and investments in education and social services can act as powerful deterrents to crime. Initiatives aimed at economic development, job training, and poverty reduction are therefore vital components of a comprehensive crime prevention strategy.
Law Enforcement Strategies
The effectiveness and approach of law enforcement agencies are paramount in shaping crime rates. In Rhode Island, strategies employed by state police, municipal police departments, and federal partners significantly influence public safety. For 2025-2026, many departments are focusing on data-driven policing, community-oriented policing, and intelligence-led investigations.
Community policing, which emphasizes building relationships between officers and residents, is believed to foster trust and encourage cooperation, leading to better crime reporting and prevention. Data-driven approaches allow for the strategic deployment of resources to areas with the highest crime activity. Intelligence-led policing focuses on identifying and disrupting criminal networks. Furthermore, the adoption of new technologies, such as advanced surveillance systems and forensic tools, also plays a role. The allocation of resources, training of officers, and the implementation of evidence-based policing practices are all critical determinants of law enforcement's impact on crime rates.
Demographic Shifts
Changes in a population's demographics can also influence crime patterns. Factors such as age distribution, population density, and migration patterns can have an impact. For example, a growing youth population, if not adequately engaged with educational and recreational opportunities, can sometimes correlate with higher rates of juvenile delinquency.
Rhode Island, like many states, experiences shifts in its population composition. Urban centers may see increased population density, which can sometimes lead to a higher concentration of certain types of crime. Conversely, suburban and rural areas might face different challenges. Understanding these demographic trends allows for more tailored public safety planning and resource allocation. The increasing diversity of Rhode Island's population also necessitates culturally sensitive approaches to law enforcement and community engagement.
Community Programs and Prevention
Beyond law enforcement, community-based programs play a crucial role in crime prevention. These initiatives often focus on addressing the root causes of crime and providing support to at-risk individuals and communities. For 2025-2026, Rhode Island continues to invest in a range of such programs.
Examples include after-school programs for youth, mentorship initiatives, job training and placement services, substance abuse counseling, mental health support, and violence interruption programs. These programs aim to provide positive alternatives to criminal behavior, foster social cohesion, and build resilience within communities. The effectiveness of these programs is often measured by their ability to reduce recidivism rates and prevent individuals from entering the criminal justice system in the first place. Strong partnerships between government agencies, non-profit organizations, and community leaders are essential for the success of these preventative efforts. You can learn more about factors influencing crime by exploring community-level initiatives.
Geographical Variations Within Rhode Island
Crime is not uniformly distributed across Rhode Island. Significant variations exist between different cities, towns, and regions, each with its unique set of challenges and characteristics. Understanding these geographical differences is key to developing targeted and effective public safety strategies.
Major Cities and Their Crime Profiles
Rhode Island's major urban centers, such as Providence, Warwick, Cranston, and Pawtucket, typically experience higher crime rates than their rural counterparts. This is a common pattern observed nationwide, often linked to higher population density, greater socioeconomic disparities, and more complex social dynamics.
Providence, as the state capital and largest city, often reports the highest numbers of both violent and property crimes. However, it's important to note that these statistics are often concentrated in specific neighborhoods. The city has seen ongoing efforts to revitalize certain areas and address crime through community policing and targeted interventions. For 2025-2026, Providence continues to grapple with issues related to gang activity, drug trafficking, and property offenses, but also benefits from extensive community programs and a robust police department.
Warwick, the second-largest city, typically exhibits a moderate crime rate, with property crimes often being more prevalent than violent ones. Its suburban character and economic diversity influence its crime profile.
Cranston and Pawtucket, situated near Providence, also face their share of crime-related challenges, often mirroring some of the issues seen in the capital but on a smaller scale. These cities are actively working on community engagement and crime reduction initiatives.
It is crucial to remember that crime statistics for cities are often presented as aggregates, and specific neighborhoods within these cities may have vastly different crime rates. Detailed local data is essential for a precise understanding.
Rural vs. Urban Crime Differences
The distinction between urban and rural crime in Rhode Island is significant. While urban areas tend to see higher volumes of crime, rural areas often face different types of challenges.
In rural parts of Rhode Island, property crimes such as burglaries and thefts from unoccupied dwellings or agricultural properties can be more prevalent. There may also be concerns related to drug-related offenses, particularly the distribution of illicit substances in less populated areas, and occasional issues with poaching or vandalism. Law enforcement in rural areas often involves smaller departments with fewer resources, requiring innovative approaches to cover vast geographical areas.
Urban areas, as discussed, face a broader spectrum of crime, including more frequent incidents of violent crime, gang activity, and complex property crimes. The density of population and the presence of more commercial establishments can also contribute to different crime patterns. For 2025-2026, the trend of increased focus on cybercrime and fraud affects both urban and rural populations, though the methods of victimization might differ.
Understanding these geographical nuances allows for the development of more effective, localized crime prevention strategies. For instance, a strategy that works well in a dense urban environment might not be suitable for a spread-out rural community.
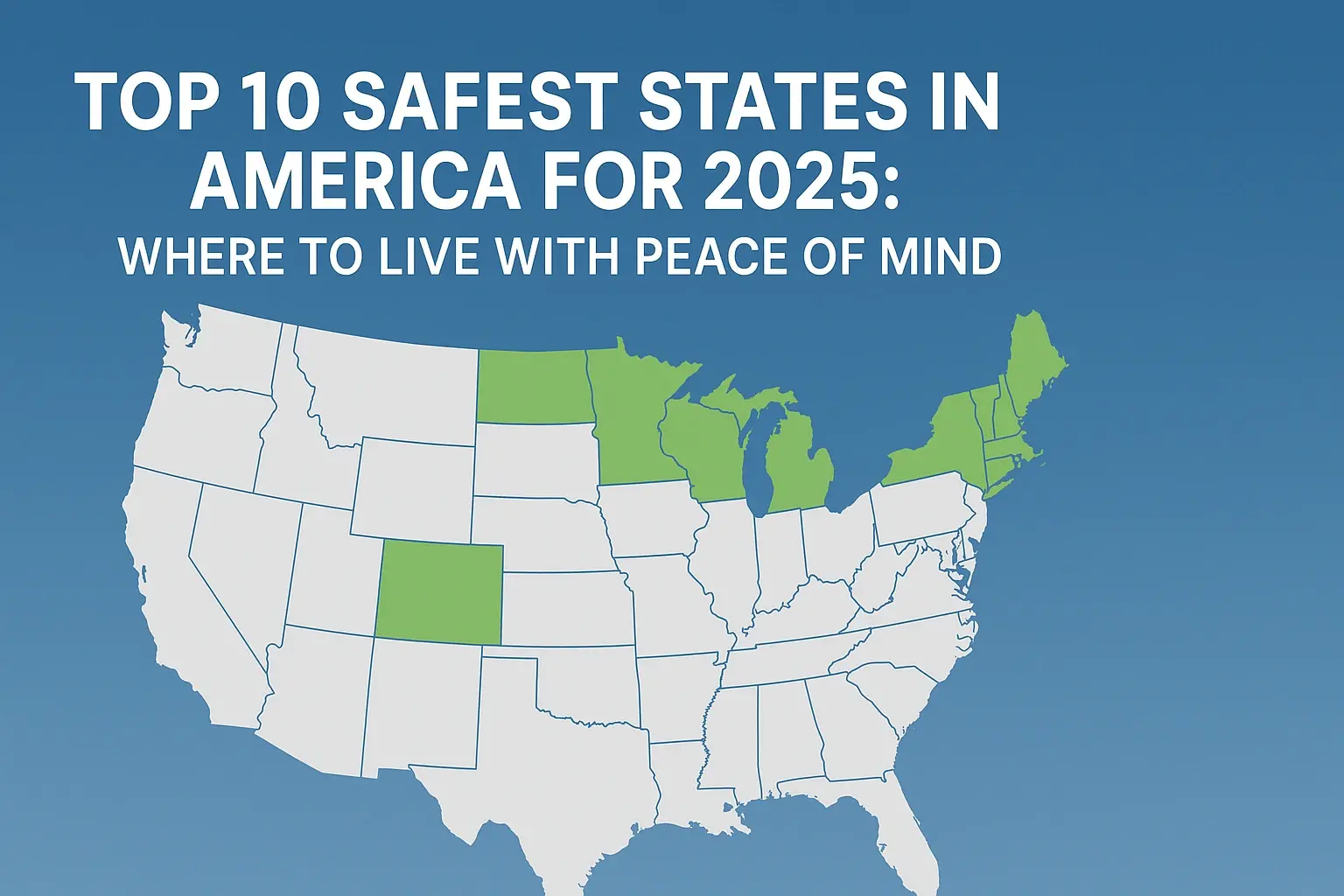
Comparing Rhode Island to National Averages
Placing Rhode Island's crime rate within the broader national context provides valuable perspective. For 2025-2026, Rhode Island generally continues to perform favorably when compared to national averages for many crime categories, particularly violent crimes.
According to preliminary data and projections, Rhode Island's violent crime rate per capita is typically lower than the national average. This includes lower rates of homicide, robbery, and aggravated assault. This can be attributed to a combination of factors, including the state's relatively smaller population, effective community policing efforts in many areas, and strong social support networks.
However, when it comes to property crime, the comparison can be more nuanced. While Rhode Island's property crime rates may be comparable to or slightly below the national average, specific categories like motor vehicle theft or burglary can fluctuate and may occasionally exceed national trends in certain localities. The impact of emerging crimes, such as sophisticated online fraud, also needs to be considered in this comparison, as national data on these offenses is still evolving.
It is important to consult the latest FBI UCR data and state-specific reports for the most accurate comparisons. Trends in national crime rates are also subject to change, influenced by nationwide economic conditions, policy shifts, and societal factors. Rhode Island's ability to maintain its lower-than-average violent crime rates while addressing property and emerging crime challenges will be a key indicator of its public safety success in the coming years. For detailed breakdowns, you can refer to recent crime statistics.
Future Outlook and Prevention Strategies
Forecasting crime trends is an inherently complex task, but by analyzing current data and understanding the driving forces, we can project potential future scenarios and outline effective prevention strategies for Rhode Island. For the period beyond 2026, several key areas will likely shape the state's crime landscape.
Continued focus on community policing: The trend towards community-oriented policing is expected to persist and likely intensify. Building trust and collaboration between law enforcement and residents is crucial for intelligence gathering, crime reporting, and fostering a sense of shared responsibility for public safety. Investments in training and resources for community policing initiatives will be vital.
Addressing root causes: As socioeconomic factors continue to be significant drivers of crime, future strategies will need to prioritize addressing root causes. This includes sustained efforts in poverty reduction, job creation, access to quality education and affordable housing, and robust mental health and substance abuse treatment programs. A holistic approach that tackles these underlying issues is more sustainable than solely relying on enforcement.
Adapting to technological advancements: The rise of cybercrime and other technology-enabled offenses will necessitate continuous adaptation. Law enforcement agencies will need to invest in advanced cyber forensics capabilities, data analytics, and training to combat evolving digital threats. Public awareness campaigns on online safety and fraud prevention will also become increasingly important.
Data-driven and evidence-based interventions: The use of data analytics to identify crime hotspots, predict trends, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions will become even more critical. Implementing evidence-based policing practices and crime prevention programs that have demonstrated success in other jurisdictions will be key to optimizing resource allocation and achieving measurable results.
Youth engagement and intervention: Focusing on early intervention programs for at-risk youth, including mentorship, educational support, and positive recreational activities, can significantly impact future crime rates. Addressing juvenile delinquency and providing pathways to success for young people is a long-term investment in community safety.
Interagency collaboration: Effective crime prevention requires strong partnerships between law enforcement, social services, educational institutions, community organizations, and the private sector. Collaborative efforts can lead to more comprehensive and impactful solutions.
The future outlook for Rhode Island's crime rate hinges on the state's ability to implement these forward-thinking, multi-faceted prevention strategies. By focusing on both immediate safety concerns and the underlying societal factors, Rhode Island can continue to strive for a safer and more secure environment for all its residents.
Conclusion: Navigating Rhode Island's Crime Landscape
The analysis of Rhode Island's crime rate for 2025-2026 reveals a complex and evolving landscape. While the state generally demonstrates favorable trends in violent crime compared to national averages, property crimes and emerging threats like cybercrime necessitate ongoing vigilance and strategic adaptation. Socioeconomic factors, law enforcement strategies, demographic shifts, and community-based programs all play integral roles in shaping the state's public safety narrative. Geographical variations further underscore the need for localized, targeted approaches.
Moving forward, Rhode Island's commitment to community policing, addressing root causes of crime through social and economic initiatives, and adapting to technological advancements will be paramount. A proactive, data-driven, and collaborative approach to crime prevention is not merely advisable but essential for fostering a safer and more secure future for all its citizens. By understanding the trends and actively implementing evidence-based strategies, Rhode Island can continue to build stronger, safer communities.